Naval Air Station Patuxent River
 Clash Royale CLAN TAG#URR8PPP
Clash Royale CLAN TAG#URR8PPP | Naval Air Station Patuxent River | |
|---|---|
Located near: Lexington Park, Maryland | |
 A P-3 Orion and P-8 Poseidon flying over NAS Patuxent River in 2010 | |
 Logo of NAS Patuxent River | |
| Type | Naval Air Station |
| Site information | |
| Owner | |
| Controlled by | |
| Condition | Active |
| Website | www.cnic.navy.mil/nas_patuxent_river |
| Site history | |
| Built | 1942-1943 |
| In use | April 1, 1943-Present |
| Garrison information | |
| Current commander | CAPT Jason Hammond, USN |
| Garrison | |
| Trapnell Field | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||||||
| Airport type | Military | ||||||||||||||||||
| Location | Patuxent River, Maryland | ||||||||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 39 ft / 12 m | ||||||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 38°17′10″N 76°24′42″W / 38.28611°N 76.41167°W / 38.28611; -76.41167Coordinates: 38°17′10″N 76°24′42″W / 38.28611°N 76.41167°W / 38.28611; -76.41167 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Map | |||||||||||||||||||
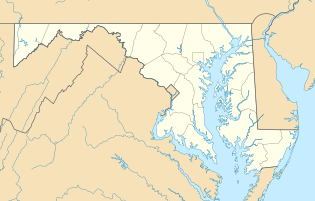 KNHK Location of Naval Air Station Patuxent River | |||||||||||||||||||
Runways | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||

A T-2C Buckeye, assigned to the U.S. Naval Test Pilot School at PAX River, used for training experienced pilots in test pilot methods
Naval Air Station Patuxent River (IATA: NHK, ICAO: KNHK, FAA LID: NHK), also known as NAS Pax River, is a United States naval air station located in St. Mary's County, Maryland, on the Chesapeake Bay near the mouth of the Patuxent River.
It is home to Headquarters, Naval Air Systems Command (NAVAIR), the U.S. Naval Test Pilot School, the Atlantic Test Range, and serves as a center for test and evaluation and systems acquisition relating to naval aviation.
Commissioned on April 1, 1943, on land largely acquired through eminent domain, the air station grew rapidly in response to World War II and continued to evolve through the Cold War to the present.
Contents
1 History
1.1 Genesis: 1937
1.2 1940s: Wartime urgency
1.2.1 Fast Track Chartering of Base and Start of Construction
1.2.2 Hardships for Original Civilian Residents
1.2.3 Rehabilitation of rail line
1.2.4 Extension of highway
1.2.5 Construction boom town
1.2.6 Foundation
1.3 1950s: Flight test centre and Test Pilot School Facilities Launched
1.4 1965: Addition of Reconnaissance Squadrons
1.5 1970s: Ongoing Development of Major Naval Aircraft
1.5.1 Renaming of the airfield
1.6 1990s: End of Cold War, base consolidations favor PAX River NAS
1.6.1 Growth
1.6.2 Film Location
1.7 2000's: Forefront of Research, development, and testing
2 Tenant Commands
3 Patuxent River Naval Air Museum
4 See also
4.1 Area Information
4.1.1 Town
4.1.2 Local off base government and services
4.1.3 Area Civilian transportation
4.1.4 Higher Education
4.1.5 Local Recreation and Tourism
5 Sources
6 References
7 External links
History
Genesis: 1937

Aerial view of NAS Patuxent River in the mid-1940s
Situated on a peninsula between the Potomac River and the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Patuxent River, NAS Patuxent River is located on 6,400 acres (26 km2) of what was once prime farmland, consisting of several large plantations, Mattapony, Susquehanna, and Cedar Point, as well as numerous tenant and sharecropper properties and a few clusters of vacation homes. The Cedar Point community included several churches, a post office, and a gas station. Some of the old homes now serve as quarters for Navy personnel stationed there.[1]
In 1937, the Navy's Bureau of Aeronautics sought to consolidate aviation test programs, previously being conducted at several stations, including Dahlgren and Norfolk, the Washington Navy Yard, Naval Air Station Anacostia in Washington, D.C., and the Naval Aircraft Factory in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Cedar Point was selected due to its remote location on the coastline, well removed from air traffic congestion, with ample space for weapons testing.[1]
1940s: Wartime urgency

A U.S. Navy Grumman TBM-3W Avenger on the ground at Naval Air Training Center, Naval Air Station Patuxent River, circa 1946

Aerial view of the hangars in the late 1940s
Fast Track Chartering of Base and Start of Construction
The onset of American involvement in World War II spurred establishment of the new air station.
Rear Admiral John Henry Towers, Chief of Bureau of Aeronautics, requested approval and authorization to begin construction on December 22, 1941. Secretary of the Navy, Frank Knox, gave approval on 7 January 1942 and construction began on 4 April 1942.
Hardships for Original Civilian Residents
The original civilian residents had about a month, until 1 March 1942, to relocate as the federal government purchased all the land at a cost of $712,287 for 6,412 acres (26 km2),[1] which in 2013 dollars would be the equivalent of being paid $1,261 per acre. Many residents were forced to sell land that had been in their families for generations. Some families had roots in the area going back 300 years. These included traditional farming, crabbing and fishing families and there were protests. National wartime urgency was however felt in Washington at the time to take precedence, and the process of eminent domain went through.
Rehabilitation of rail line
A lack of transportation in Saint Mary's County led the Navy to acquire and revitalize a branchline called the Washington, Brandywine and Point Lookout Railroad (aka "The Farmers' Railroad") from Brandywine to Mechanicsville, Maryland, in June 1942 and build an extension south from Mechanicsville to the air station. Known as the U.S. Government Railroad, the rail line was steam-powered and operated south of Brandywine for exclusive official use until 1954, when the Pennsylvania Railroad assumed operation of the line. Rail service ended in 1965, and the line was subsequently scrapped, although the right-of-way is still very visible.
Extension of highway
A highway extension to the new air station was required by the project—250,000 tons of material were transported by either truck or water routes during a year of construction.[1]
Construction boom town
Employing some 7,000 at its peak of construction, the area had a Gold Rush "boom town" feel as local residents were joined by workers from all over the country, eager to get on the high-paying jobs on station.[1]
Foundation
On 20 October 1942, U.S. Marines first arrived and took over security. Today, the station utilizes Navy Masters-At-Arms (MA) and Navy Civilian Police Department of Defense Police for standard local law enforcement and the Naval Criminal Investigative Service (NCIS) for high-profile criminal investigations.
During construction, housing needs far outstripped supply, and barracks were built for workers on the station. Later, several housing areas were erected off station for workers and their families in Lexington Park, formerly Jarboesville, named in honor of the USS Lexington, the Navy's second aircraft carrier, lost during the Battle of the Coral Sea on 8 May 1942.[1] The town's expansion had begun.

Photo of the commissioning of the Lockheed PO-1W Warning Star by the U.S. Navy air development squadron VX-4 Vanguards at Naval Air Station Patuxent River, Maryland (USA), circa 1949

A Vought XF7U-1 Cutlass prototype being photographed by the press on 18 November 1948 at the Naval Air Test Center at Naval Air Station Patuxent River, Maryland (USA)
The station was formally commissioned "U.S. Naval Air Station, Patuxent River, Maryland" on 1 April 1943. In a ceremony presided over by RADM John S. McCain, Sr., then chief of the Bureau of Aeronautics, Patuxent River was referred to as "the most needed station in the Navy."[2] The unofficial name had been Cedar Point or the Naval Air Station at Cedar Point, but officials were concerned about possible confusion with the Marine Corps Air Station Cherry Point, North Carolina, so the new facility was named for the adjacent river.
In 1945 the Test Pilot School was established with the Navy's Flight Test Group transferred from Naval Air Station Anacostia, Washington, DC to NAS Patuxent River.[1]
1950s: Flight test centre and Test Pilot School Facilities Launched
The base became a centre for testing as several facilities were constructed throughout the 1950s and 1960s; including the facilities for United States Naval Test Pilot School (1958), the Weapons Systems Test Division (1960), and the Propulsion System Evaluation Facility. The base also served as the testing facility for the V-22 Osprey.
In addition to its role in testing naval aircraft, during the 1950s to 1970s Patuxent River served as an operational base for a Transport Squadron - VR-1, a TACAMO squadron - VQ-4, Airborne Training Unit Atlantic - AEWTULANT, and VW-11, VW-13 AN VW-15 and a number of Patrol Squadrons including VP-8, VP-44, VP-49, VP-24, VP-30 and VP-68.
1965: Addition of Reconnaissance Squadrons

Hellenic AF (Greek) RF-4 Phantom reconnaissance fighter with gear down. RF-4s underwent electronic warfare testing at PAX River in the 1960s. British Phantom FGR.2s were known to visit PAX at the time.
By 1965, reconnaissance Squadron VQ-4, based at NAS Patuxent River, began using Lockheed C-130s equipped with special communications equipment to perform their around-the-clock Take Charge and Move Out (TACAMO) mission. VQ-4 provided long-range, very-low-frequency communications relay between the National Command Center and the ballistic missile submarine fleet. Two A-7A Corsair II aircraft made the transatlantic crossing from NAS Patuxent River to Évreux, France, in 1967, racking up 3,327 nautical miles in just over seven hours, an unofficial long distance, non-refueled flight by light attack jet aircraft.
Cooperation with the British also led to transatlantic visits to PAX River by RAF squadrons.

Engineering design sketch of McDONNELL DOUGLAS BAe_AV 8B HARRIER, that underwent development and testing at PAX River NAS

F-14 Tomcat in flight. Tomcats underwent major development and testing at PAX.

V-22 Osprey in test flight with Lexington Park, Maryland in background
Research and development at NAS Patuxent River forged ahead in the 1970s. The Grumman F-14 Tomcat, the McDonnell Douglas AV-8B Harrier II jump jet, and the Lockheed P-3 Orion were just a few of the major aircraft programs undergoing the rigorous test and evaluation process at NAS Patuxent River. Helicopter programs also achieved major milestones during the 1970s. The Naval Air Test Center (NATC) at NAS Patuxent River took part in helicopter development and testing for new roles, such as minesweeping. The final flight of the service acceptance trials for the Bell AH-1 SuperCobra gunship were made at NATC Patuxent River.
Renaming of the airfield
On 1 April 1976, Patuxent River's airfield was named after pioneering aviator VADM Frederick M. Trapnell, a former commander of the Naval Air Test Center at the station. Keynote address speaker, ADM Frederick H. Michaelis, Chief of Naval Material, noted: "All who fly in Navy blue remain indebted to Vice Admiral Trapnell. This field will serve as a living reminder of that debt."[3]
1990s: End of Cold War, base consolidations favor PAX River NAS
Growth
Since the end of the Cold War, the Pentagon's Base Realignment and Closure measures have migrated research and testing facilities for both rotary and fixed-wing aircraft to NAS Patuxent River from decommissioned bases. The complex now hosts over 17,000 people, including active-duty service members, civil-service employees, defense contractor employees, and military dependents.[citation needed]
Film Location
The base was also used as a filming location for the Harrison Ford film Random Hearts (1999). Ford and director Sydney Pollack both visited Naval Air Station Patuxent River. Ford, a certified pilot, flew the aircraft himself.
2000's: Forefront of Research, development, and testing
In January, 1992, the PAX River Station acquired the Aircraft Division of the Naval Air Warfare Center (NAWCAD). Naval Test Wing Atlantic (NTWL) was already located there. NAWCAD was a branch of the Naval Air Warfare Center, created in 1991, and located in Washington, DC. Its mission was the development and improvement of weapons. The partnership of these two units led to a flourishing of aircraft research and development at Patuxent.
A number of new laboratory facilities on the forefront of research were created:[4] a Manned Flight Simulator, the Aircraft Anechoic Test Facility, the Air Combat Environment Test and Evaluation Facility, the Aircraft Test and Evaluation Facility, the Captain Steven A. Hazelrigg Flight Test Facility. The physical plant was expanded by new construction: the U.S. Naval Test Pilot School academic building, an Aviation Survival Training Center pool facility and a new Air Traffic Control Tower. The base has not been slow in social advancement, either. In 2013, a new, large-size Child Development Center (CDC) was completed. On 18 September 2014, Captain Heidi Flemming became the first female commanding officer of NAS Patuxent River.[5]
For the future, the researchers are looking in the direction of unmanned flight.
Tenant Commands

F-35 Fighter, which is under testing at PAX River NAS
- Naval Air Systems Command
- U.S. Naval Test Pilot School
- Air Test and Evaluation Squadron 1
- Scientific Development Squadron 1
- Air Test and Evaluation Squadron 20
- Rotary Wing Test Squadron 21
- Air Test and Evaluation Squadron 23
.

X-35C on display at the Patuxent River Naval Air Museum, the X35C underwent testing at PAX River

Kate Morrand, an artifact conservator at Naval History and Heritage Command, inspects a piece of pottery recovered from the wreck of the sloop-of-war USS Scorpion. The ship was scuttled in the Patuxent River during the War of 1812 to avoid capture by British forces. (U.S. Navy photo)

100422-N-5549O-101 PATUXENT RIVER, MD. Friday, 22 April 2010, Naval Aviators Cdr. Beau Duarte and Lcdr. Tom Weaver sit in the cockpit F/A-18 "Super Hornet" following a supersonic flight test, powered by a 50/50 blend of biofuel. The test, conducted at Naval Air Station Patuxent River, MD., drew hundreds of onlookers.
The Patuxent River Naval Air Museum adjoins the base and can be accessed by the general public without coming onto the main base.
Patuxent River Naval Air Museum official website

A U.S. Navy X-47B Unmanned Combat Air System (UCAS) demonstrator completes its first shore-based arrested landing at Naval Air Station, Patuxent River, Md., 4 May 2013. The UCAS used a tailhook to catch a MK-7 arresting gear to quickly stop.

Patuxent River, Md. (3 August 2005) – The pilot of a T-38A Talon, assigned to the U.S. Naval Test Pilot School. Thumbs up!
- See: U.S. Navy Museum and Other Navy Museums
See also
Area Information
Town
The base is located adjacent to Lexington Park, Maryland
Local off base government and services
The town is unincorporated and is under the Saint Mary's County government which also provides all municipal services.
Area Civilian transportation
Limited local buses are provided through St. Mary's Transit [1], and commuter bus service to Washington, D.C. is provided by MTA [2].
The nearest commercial airports are Reagan National Airport in Washington D.C. and Baltimore Washington International Airport (BWI) in suburban Baltimore.
St. Mary's County is also served by a civilian general aviation airport called Captain Walter Duke Regional Airport near Leonardtown, Maryland
Higher Education
- Nearby St. Marys College of Maryland is ranked 4th in the nation under the category "Best Colleges for Veterans" [6] by U.S. News & World Report college rankings.[7]
- It is also ranked 5th in the nation under the category "Public Colleges".[8] It's admissions standards are however, rigorous.[8]
- St. Marys College also has extensive "open to the public" evening and weekend educational enrichment programs, including public lectures, seminars, films and special events. It also hosts a summer writing workshop
College of Southern Maryland is a regional community college, it has a training center near the base in Lexington Park and a main campus 15 miles away in Leonardtown, Maryland
Southern Maryland Higher Education Center in California, Maryland.
Paul Hall Center for Maritime Training and Education is a Merchant Marine school in nearby Piney Point, Maryland.
Local Recreation and Tourism
Point Lookout State Park nationally recognized natural area and historic site; former Civil War prison camp, beaches, fishing, camping
St. Mary's City site of first settlement in the Maryland colony, four museums and reconstructed colonial town and living history center (7 miles from base)
Patuxent River Naval Air Museum Naval aviation history, including history of test pilots and naval aviation development at PAX River NAS, many aircraft on display
Solomons Island Naval recreation facility in nearby Solomons Island Maryland (reachable by bridge)
Sotterley Plantation reconstructed plantation, pre-Civil War history museum
USS Tulip monument and federal grave site for Civil War sailors who died in the explosion of a Union gunship in area waters in 1864- Point Lookout Light House
- Piney Point Lighthouse and Museum
Cecils Old Mill museum, art gallery and artists coop in nearby Great Mills, Maryland
National Register of Historic Places listings in St. Mary's County, Maryland many buildings date back to the 1600 and 1700s
Leonardtown county seat, historic town dating back to the 1600s
Tudor Hall, St. Marys County Historical Society (limited hours)
Sources
FAA Airport Master Record for NHK (Form 5010 PDF)
References
^ abcdefg Naval Air Systems Command Headquarters, Strategic Planning Division, "The History of Naval Air Station Patuxent River, Maryland," undated, but circa 2000.
^ "Patuxent River". Retrieved 2009-05-02.
^ "In the center of change: Frederick M. Trapnell". Retrieved 2009-05-02. [permanent dead link]
^ "History of the Naval Air Station". Naval Air Station Patuxent River. Commander, Navy Installation Command (CNIC). Retrieved 15 August 2017.
^ http://www.thebaynet.com/articles/0914/pax-river-command-changes-to-first-woman-co.html
^ "National Liberal Arts- Colleges Summary: St. Mary's College of Maryland" U.S. News & World Report Best Colleges and Universities Ranking, 2014 http://colleges.usnews.rankingsandreviews.com/best-colleges/rankings/national-liberal-arts-colleges/veterans
- Colleges Summary: St. Mary's College of Maryland" U.S. News & World Report Best Colleges and Universities Ranking, 2014 http://colleges.usnews.rankingsandreviews.com/best-colleges/rankings/national-liberal-arts-colleges/veterans
^ "National Liberal Arts Colleges Summary: St. Mary's College of Maryland" U.S. News & World Report Best Colleges and Universities Ranking, 2014 http://colleges.usnews.rankingsandreviews.com/best-colleges/rankings/national-liberal-arts-colleges/veterans
^ ab "National Liberal Arts Colleges Summary: St. Mary's College of Maryland" U.S. News & World Report Best Colleges and Universities Ranking, 2014 http://colleges.usnews.rankingsandreviews.com/best-colleges/st-mary-s-college-of-maryland-163912/overall-rankings
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Naval Air Station Patuxent River. |
Military
- Naval Air Systems Command (NAVAIR)
- Naval Air Warfare Center Aircraft Division
NAS Patuxent River, Globalsecurity.org
FAA Airport Diagram (PDF), effective August 16, 2018- Resources for this U.S. military airport:
- FAA airport information for NHK
- AirNav airport information for KNHK
- ASN accident history for NHK
- NOAA/NWS latest weather observations
- SkyVector aeronautical chart for KNHK
- FAA airport information for NHK
Area Recreation and attractions
- St. Mary's County Travel and Tourism
Historic St. Marys City Site of first settlement of Maryland Colony, museums and reconstructed colonial town
Solomons Island Naval recreation facility in nearby Solomons Island Maryland (reachable by bridge)
United States Colored Troops Memorial Statue memorial to 700 African-American soldiers and sailors from St. Mary's County, Maryland who served in the Union forces during the American Civil War. Includes an educational display. Recreational community park setting. Special celebrations as well.
